Do the vaccines prevent you from infection or transmitting it?
// Plays video from Fauci (which I couldn’t find a link to, but it’s in the presentation)
95% chance you will not get symptomatic infection… until we prove that the vaccine prevents transmission… people who are vaccinated should wear a mask around those who might be vulnerable to infection.
~ Fauci
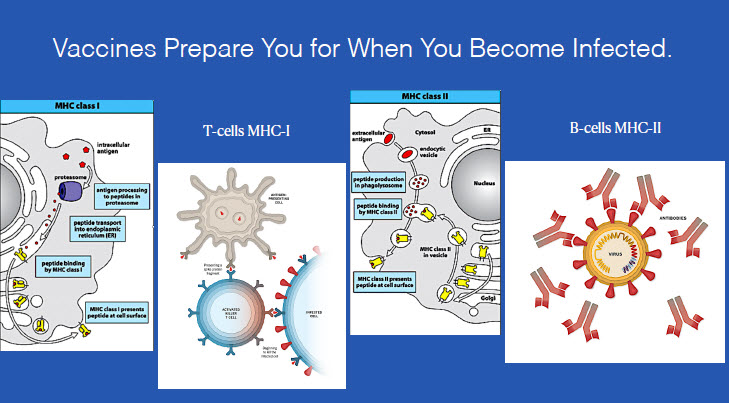
Vaccines work because they prime your body to be ready when you are infected. Something comes in, it’s an antigen; a vaccine – a protein that is foreign to your body, comes in, gets broken down in the cells, gets presented to the MHC-I, where the T-cells will recognize it, and they get activated and they look for other cells that are infected that also have this antigen presented.
They release chemicals, cause damage, cause inflammation, and cause blood-clotting. To “kill” the invading organism. Except in this case there’s no actual invading organism. You injected it into yourself.
The pieces that go out, whether that’s the whole virus or the vaccine, and in this case, the spike protein, come back into other cells, those cells will pick them up with MHC-II (3-5 days), a little bit later on (7-10 days), Beta cells recognize MHC-II, and make antibodies. So anything outside in the bloodstream, the antibodies will go and attack, and take them out of commission so they can’t attach to you and cause harm. That’s what vaccines do.
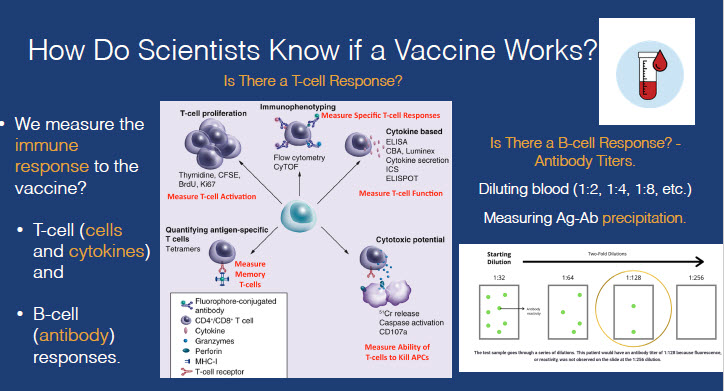
They cause you to make T-cell & B-cell responses, that you will form memory cells to. We do not want T-cell and antibodies floating around your bloodstream forever.





![[Comedy/Truth] The Narrative is Crumbling – 16 Reasons Why (JP Sears)](https://pennybutler.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/jpsears-narrativecrumbling.jpg)
![[Italy] What’s in the Blood? 1,006 Jabbed Patients [Dark-Field Paper -Pfizer/Moderna]](https://pennybutler.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/DarkField1006-ItalianStudy-594x437.jpg)