Finally, an Australian paper on COVID Vaccines…
- Updated:2 years ago
- Reading Time:45Minutes
- Post Words:11197Words
Journal of Clinical & Experimental Immunology, Published: 21 Sep 2022. New Australian paper calls out the severe side effects and false covid information from government agencies.
The effects of these vaccinations are slowly becoming apparent after millions of people have been vaccinated as often as four times within a year. This review has been written from an Australian perspective with the main focus on the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. We will look at the promises and predictions originally made and the actual facts. We will evaluate the safety and efficacy by looking at the literature and the data from government agencies. The literature review will be summed up in a table listing the so far reported side effects, many of which are very serious, including death, with this data coming from 1011 case reports. Long-term side effects will also be covered, and the risk-benefit ratio will be explored. The review is ending with some very critical questions that need further discussion.
COVID-19 vaccines – An Australian Review | Journal of Clinical & Experimental Immunology | Conny Turni, Astrid Lefringhausen | Submitted: 10 Sep 2022; Accepted: 12 Sep 2022; Published: 21 Sep 2022
I’ve just gone through and highlighted the whole paper, if you want to browse by image whilst waiting for the summary – click on an image and scroll through with the arrows. It might be hard to read given that it doesn’t go fullscreen on computers, so I’ll also upload the images to my Telegram channel if you want to download or read them there.
ISSN: 2475-6296
Queensland Alliance for Agriculture and Food Innovation, the University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland 4067, Australia.
COVID-19 “Vaccines” available in Australia:
- mRNA technology: Comirnaty (Pfizer)
- mRNA technology: Spikevax (Moderna)
- vector dna technology: Vaxzevria (AstraZeneca)
- vector dna technology: Johnson & Johnson (Janssen)
- and Nuvaxoid (Novavax) which contains a modified spike derived from moth cells cultured after transfection using Baculovirus, which express the spike protein on their cell membrane. This spike protein is harvested and assembled onto a synthetic lipid nanoparticle, which displays 14 spike proteins each. (https://www.precisionvaccinations.com/vaccines/novavax-covid-19-vaccine).
Every one of these vaccines forces the vaccinees body to produce the spike protein for which the genetic code is delivered into the cells as mRNA via a nanoparticle or as double stranded DNA via a viral vector.
(https://www.tga.gov.au/international-covid-19-vaccines-recognised-australia)
- The government continues to push particularly the mRNA vaccinations by encouraging a fourth vaccination and recommending the vaccine for pregnant women as well as children 5 to 11 years old.
- The official public message is that the mRNA vaccines are safe.
- However, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), the medicine and therapeutic regulatory agency of the Australian Government, states quite clearly on their website that the large-scale trials are still progressing and no full data package has been received from any company.
- The TGA is currently getting rolling data and safety and effectiveness are still being assessed (https://www.tga.gov.au/covid-19-vaccines-undergoing-evaluation).
- However, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), the medicine and therapeutic regulatory agency of the Australian Government, states quite clearly on their website that the large-scale trials are still progressing and no full data package has been received from any company.
The mRNA vaccines were supposed to remain at the injection site and be taken up by the lymphatic system. This assumption proved to be wrong.
- During an autopsy of a vaccinated person that had died after mRNA vaccination it was found that the vaccine disperses rapidly from the injection site and can be found in nearly all parts of the body (01)1. Hansen, T., Titze, U., Kulamadayil-Heidenreich, N. S. A., Glombitza, S., Tebbe, J. J., Röcken, C., & Wilkens, L. (2021). First case of postmortem study in a patient vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, … Click for full citation.
- The mRNA is enveloped in liquid nanoparticles (LNP) containing a mixture of phospholipids, cholesterol, PEGylated lipids and cationic or ionizable lipids (02) 2. Ndeupen, S., Qin, Z., Jacobsen, S., Bouteau, A., Estanbouli, H., & Igyártó, B. Z. (2021). The mRNA-LNP platform’s lipid nanoparticle component used in preclinical vaccine studies is highly inflammatory. Iscience, 24(12), 103479. .
- Research has shown that such nanoparticles can cross the blood-brain barrier (03) 3. Zhou, Y., Peng, Z., Seven, E. S., & Leblanc, R. M. (2018). Crossing the blood-brain barrier with nanoparticles. Journal of controlled release, 270, 290-303. and the blood-placenta barrier (04) 4. Wick, P., Malek, A., Manser, P., Meili, D., Maeder-Althaus,X., Diener, L., … & von Mandach, U. (2010). Barrier capacity of human placenta for nanosized materials. Environmental health perspectives, 118(3), 432-436.
There are multiple ways in which the virus and the spike protein can spread throughout the body and from cell to cell without attracting too much attention from the immune system.
- Further weakening of the immune system through rashly promoted genetic intervention can only lead to more severe disease.
So it came as no surprise that the European Medicines Agency assessment report for the Moderna vaccine on page 47 (https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/assessment-report/spikevax-previously-covid-19-vaccine-moderna-epar-public-assessment-report_en.pdf) also noted that mRNA could be detected in the brain following intramuscular administration at about 2% of the level found in plasma.
In 2021 researchers from Japan reported a disproportionately high mortality due to cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and intracranial haemorrhage. Despite not being able to prove a causal link with vaccines, as no autopsies were performed, they still believed that a link with vaccination is possible and further analysis is warranted (05) 5. Shimazawa, R., & Ikeda, M. (2021). Potential adverse events in Japanese women who received tozinameran (BNT162b2, Pfizer-BioNTech). Journal of Pharmaceutical Policy and Practice, 14(1), 1-3. .
It was stated that the mRNA will degrade quickly.
- Normally, mRNA breaks down within a few minutes to hours, however, the mRNA in these vaccines is nucleoside-modified to reduce potential innate immune recognition (06) 6. Karikó, K., Buckstein, M., Ni, H., & Weissman, D. (2005). Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: the impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity, 23(2), 165-175. (07)7. Karikó, K., Muramatsu, H., Welsh, F. A., Ludwig, J., Kato, H., Akira, S., & Weissman, D. (2008). Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA yields superior nonimmunogenic vector with increased translational capacity and biological stability. … Click for full citation and it has been shown that production of the spike protein in some vaccines is kept up for an extraordinarily long time.
- A study by Röltgen et al. (08)8. Röltgen, K., Nielsen, S.C.A., Silv,a O., Younes, S.F. et al. (2022). Immune imprinting, breadth of variant recognition, and germinal center response in human SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. Cell, 185, 1025 – 1040. DOI: … Click for full citation found that the vaccine mRNA persists in the body up to 60 days, with 60 days being the end point of their study.
- It is thus unknown and impossible to define how much of the spike protein is actually produced in the vaccinated.
- It is impossible to assess how much spike protein any individual vaccinee produces following an inoculation.
- A study by Röltgen et al. (08)8. Röltgen, K., Nielsen, S.C.A., Silv,a O., Younes, S.F. et al. (2022). Immune imprinting, breadth of variant recognition, and germinal center response in human SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. Cell, 185, 1025 – 1040. DOI: … Click for full citation found that the vaccine mRNA persists in the body up to 60 days, with 60 days being the end point of their study.
If a blood vessel is directly injected, the nanoparticles will travel in minutes to all major organs including the brain.
- It is unknown where exactly the vaccine travels once it is injected, and how much spike protein is produced in which (and how many) cells.
Prominent cardiologist Dr Peter McCullough stated that the spike protein – a cytotoxin solely responsible for the severity of the respiratory infection – makes the use of it as immunizing agent dangerous.
- The spike protein in itself can produce COVID- 19 symptoms as shown in animal experiments.
- The S1 subunit of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein when injected into transgenic mice overexpressing human ACE-2 caused a COVID-19 like response (a decline in body weight, dramatically increased white blood cells and protein concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), upregulation of multiple inflammatory cytokines in BALF and serum, histological evidence of lung injury, and activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) pathways in the lung (09)9. Biancatelli, R. M. C., Solopov, P. A., Sharlow, E. R., Lazo, J. S., Marik, P. E., & Catravas, J. D. (2021). The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunit S1 induces COVID-19-like acute lung injury in ?18-hACE2 transgenic mice and barrier dysfunction … Click for full citation.
- It was further shown that the spike protein S1 subunit, when added to red blood cells in vitro, could induce clotting by binding fibrinogen and ACE2 on platelets, thus triggering their aggregation (10) 10. Zhang, S., Liu, Y., Wang, X., Yang, L., Li, H., Wang, Y., … & Hu, L. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 binds platelet ACE2 to enhance thrombosis in COVID-19. Journal of hematology & oncology, 13(1), 1-22. .
- The S protein also increases human cell syncytium formation, removes lipids from model membranes and interferes with the capacity of high-density lipoprotein to exchange lipids (11)11. Cattin-Ortolá, J., Welch, L. G., Maslen, S. L., Papa, G., James, L. C., & Munro, S. (2021). Sequences in the cytoplasmic tail of SARS-CoV-2 Spike facilitate expression at the cell surface and syncytia formation. Nature communications, … Click for full citation. (12)12. Cheng, Y. W., Chao, T. L., Li, C. L., Wang, S. H., Kao, H. C., Tsai, Y. M., … & Yeh, S. H. (2021). D614G substitution of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein increases syncytium formation and virus titer via enhanced furin-mediated spike cleavage. … Click for full citation
- An in silico study showed that the spike protein S2 subunit specifically interacts with BRCA-1/2 and 53BP1 (13) 13. Singh, N., & Singh, A. B. (2020). S2 subunit of SARS-nCoV-2 interacts with tumor suppressor protein p53 and BRCA: an in silico study. Translational Oncology, 13(10), 100814. .
- BRCA-1 is frequently mutated in breast cancer in women and prostate cancer in men, while 53BP1 is a well-established tumor suppressor protein.
- The suppression of the interferon response by the mRNA vaccines can reduce the immune system’s ability to not only fight disease but to keep tumors and autoimmune reactions suppressed (14) 73. Passegu, E., Ernst, P.A. (2009). IFN-alpha wakes up sleeping hematopoietic stem cells Natural Medicine, 15 (6), Article 612613, 10.1038/nm0609-612 .
A paper published by Liu et al. conducted single-cell mRNA sequencing of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) harvested from patients before and 28 days after the first injection of a COVID-19 vaccine (15) 14. Liu, J., Wang, J., Xu, J., Xia, H., Wang, Y., Zhang, C., …& Liu, Z. (2021). Comprehensive investigations revealed consistent pathophysiological alterations after vaccination with COVID-19 vaccines. Cell discovery, 7(1), 1-15. .
- While this vaccine was based on an attenuated virus and not a mRNA vaccine, it also is injected directly into the deltoid muscle, bypassing the mucosal and vascular barriers.
- The authors found consistent alteration of gene expression following vaccination in many different immune cell types.
- One housekeeping gene of high importance is RNA polymerase I (POL I) which transcribes ribosomal DNA into RNA and monitors rDNA integrity in the process.
- Many of the downregulated genes identified by Liu et al. (2021) were linked to the cell cycle, telomere maintenance, and both promoter opening and transcription of POL I, indicative of impaired DNA repair processes .
Seneff et al (2022) describe another mechanism by which the mRNA vaccines could interfere with DNA repair (16) 15. Seneff, S., Nigh, G., Kyriakopoulos, A. M., & McCullough, P. A. (2022). Innate immune suppression by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinations: The role of G-quadruplexes, exosomes, and MicroRNAs. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 164, 113008. .
- The microRNA miR-148 has been shown to downregulate homologous recombination in the G1 phase of the cell cycle.
- MiR-148 is one of two microRNAs found in exosomes released by human cells following SARS-CoV-2 spike protein synthesis in the experiments by Mishra and Banerjea (17) 16. Mishra, R., Banerjea, A.C. (2021) SARS-CoV-2 Spike Targets USP33-IRF9 Axis via Exosomal miR-148a to Activate Human Microglia. Frontiers in Immunology, 12. DOI=10.3389/fimmu.2021.656700 .
(see also this related post (different study): Spike Protein Goes To Nucleus And Impairs DNA Repair)
It is an amazing fact that natural immunity is completely disregarded by health authorities around the world.
- We know from SARS-CoV-1 that natural immunity is durable and persists for at least 12-17 years (18) 17. Reiss, K., & Bhakdi, S. (2020). Corona, False Alarm?: Facts and Figures. Chelsea Green Publishing.
- Immunologists have suggested that immunity to SARS-Cov-2 is no different.
- The human population has encountered and co-existed with a great number of coronaviruses throughout evolution.
- Most of us have cross-reacting T-cells, B cells and antibodies derived from encounters with common cold coronaviruses that can recognise SARS-CoV-2 (19) 18. Doshi, P. (2020). Covid-19: Do many people have pre-existing immunity?. Bmj, 370. (20) 19. Ng, K. W., Faulkner, N., Cornish, G. H., Rosa, A., Harvey, R., Hussain, S., … & Kassiotis, G. (2020). Preexisting and de novo humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in humans. Science, 370(6522), 1339-1343. (21) 20. King, E. M. (2020). T-cells Are the Superstars in Fighting COVID-19. But Why are some People So Poor at Making Them?. bmj, 370.
- The human population has encountered and co-existed with a great number of coronaviruses throughout evolution.
- Immunologists have suggested that immunity to SARS-Cov-2 is no different.
- A survey of more than 100 immunologists, infectious-disease researchers and virologists working on the coronavirus, who were asked whether the virus could be eradicated, showed that almost 90% of respondents believe that the coronavirus will become endemic (22) 21. Phillips, N. (2021). The corona virus will become endemic. Nature, 590: 382-384.
- The four human coronaviruses that cause common colds are also endemic, without there ever having been a vaccine for any of them.
- The existence of related viruses might explain that approximately 40% to 45% of COVID infected people are asymptomatic and about 80% of COVID cases are mild infections.
- In some cohorts, the asymptomatic infection figure jumps as high as 96% depending on the age and cross-immunity imparted by other viruses such as beta coronaviruses HCoV-OC43 and HCoV-HKU1, which have been proposed as a mitigating factor in the spread of SARS-CoV-2 (23) 22, 10791. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910791. (24) 23. Oran, D.P., Topol, E.J. (2021). The Proportion of SARS-CoV-2 Infections That Are Asymptomatic : A Systematic Review. Annual Interntional Medicines, 174(5): 655-662. doi: 10.7326/M20-6976.
The Brownstone institute has established the most updated and comprehensive library list of 150 of the highest-quality, complete, and robust scientific studies and evidence reports/position statements on natural immunity as compared to the COVID-19 vaccine-induced immunity.
- The consensus of these studies is that immunity induced by COVID infection is robust and long lasting (https://brownstone.org/articles/79-research-studies-affirm-naturally-acquired-immunity-to-covid-19-documented-linked-and-quoted/).
When comparing the immune response to vaccination and natural infection, differences in the responses were detected.
- For example, a strong upregulation of genes associated with type I interferon production, cytotoxicity and an increase in circulating plasmablasts were only observed after natural infections (25) 24. Ivanova, E., Devlin, J., Buus, T., Koide, A., Cornelius, A., Samanovic, M., … & Koralov, S. B. (2021). Discrete immune response signature to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination versus infection. .
- In contrast, mRNA vaccines seem to suppress interferon responses (26) 25. Seneff, S. and Nigh, G. (2021). Worse than the disease? Reviewing some possible unintended consequences of the mRNA vaccines against COVID-19. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 2, 38 – 79. .
- A literature review by Cardozo and Veazev (27) 26. Cardozo, T., & Veazey, R. (2021). Informed consent disclosure to vaccine trial subjects of risk of COVID-19 vaccines worsening clinical disease. International journal of clinical practice, 75(3), e13795. concluded that COVID-19 vaccines could potentially worsen COVID-19 disease through antibody-dependent enhancement when natural infection occurs after vaccination, regardless of the delivery mechanism – vector or LNP containing RNA – of the nucleic acid coding for the spike protein.
A retrospective cohort study from Sweden revealed that individuals who survived and recovered from a previous infection had a lower risk of COVID-19 re-infection and hospitalisation for up to 20 months.
- The authors concluded that both previous infection and vaccination should be sufficient proof of immunity to COVID-19 (28)27. Nordström, P., Ballin, M., & Nordström, A. (2022). Risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection and COVID-19 hospitalisation in individuals with natural and hybrid immunity: a retrospective, total population cohort study in Sweden. The Lancet Infectious … Click for full citation (29)28. Nordström, P., Ballin, M., & Nordström, A. (2022). Risk of infection, hospitalisation, and death up to 9 months after a second dose of COVID-19 vaccine: a retrospective, total population cohort study in Sweden. The Lancet, 399(10327), … Click for full citation .
When comparing 2,653 fully vaccinated individuals with 4,361 individuals recovered from COVID-19, initial levels of antibodies were higher in the vaccinated but decreased exponentially and much faster than in individuals recovered from COVID-19 (30) 29. Israel, A., Shenhar, Y., Green, I., Merzon, E., Golan-Cohen, A., Schäffer, A. A., … & Magen, E. (2021). Large-scale study of antibody titer decay following BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine or SARS-CoV-2 infection. Vaccines, 10(1), 64. .
- There have been discussions about risk and value of vaccination in the previously infected part of the population.
- Study results have shown that the second dose in people already exposed to the virus leads to a reduction of cellular immunity, inferring those individuals previously infected with COVID-19 should not get a second injection (31)30. Lozano-Ojalvo, D., Camara, C., Lopez-Granados, E., Nozal, P., del Pino-Molina, L., Bravo-Gallego, L. Y., … & Ochando, J. (2021). Differential effects of the second SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine dose on T cell immunity in naive and COVID-19 … Click for full citation.
All of these facts should have led to the standard operating procedure of establishing antibody titres in patients before vaccination for SARS CoV-2, similar to other vaccinations.
- However, this did not happen and natural immunity is still not accepted as proof of immunity in Australia.
The vaccine was never meant to prevent the spread of the virus, but to decrease disease severity.
- A study at the University of California followed up on infections in the workforce after 76% had been fully vaccinated with mRNA vaccines by March 2021 and 86.7% by July 2021. In July 2021 75.2% of the fully vaccinated workforce had symptomatic COVID (32) 31. Keehner, J., Binkin, N.J., Laurent, L.C., Pride, D. (2021). Resurgence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Highly Vaccinated Health System Workforce. The New England Journal of Medicine, 385, 1330-1332. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMc2112981. .
Paul Elias Alexander pointed out this troubling situation in an article published by the Brownstone Organisation by citing three studies where we see this emerging situation of the vaccinated increasingly being infected and transmitting the virus.
- The study by Chau et al. reported a seminal nosocomial outbreak occurring in fully vaccinated Hospital Care workers (HCW) in Vietnam in 2021 (33)32. Chau, N. V. V., Ngoc, N. M., Nguyet, L. A., Quang, V. M., Ny, N. T. H., Khoa, D. B., … & OUCRU COVID-19 research group. (2021). An observational study of breakthrough SARSCoV-2 Delta variant infections among vaccinated healthcare workers … Click for full citation.
- The second study described an outbreak in a Finnish hospital where the virus spread among HCWs and patients (34)33. Hetemäki, I., Kääriäinen, S., Alho, P., Mikkola, J., Savolainen-Kopra, C., Ikonen, N., Nohynek, H., Lyytikäinen, O. (2021). An outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant (B.1.617.2) in a secondary care hospital in Finland, May 2021. … Click for full citation.
- In this study the Delta variant of the virus was introduced by an inpatient. Both symptomatic and asymptomatic infections occurred among vaccinated HCWs. Secondary transmissions were observed from those with symptomatic infections despite the use of personal protective equipment. The third publication detailed an outbreak in an Israeli hospital, where the virus spread among vaccinated HCWs and vaccinated patients (35) 34. Shitrit, P., Zuckerman, N. S., Mor, O., Gottesman, B. S., & Chowers, M. (2021). Nosocomial outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in a highly vaccinated population, Israel, July 2021. Eurosurveillance, 26(39), 2100822. . (https://brownstone.org/articles/79-research-studies-affirm-naturally-acquired-immunity-to-covid-19-documented-linked-and-quoted/).
Acharya et al. (2021) and Riemersma et al. (2021) both showed that the vaccinated have very high viral loads similar to the unvaccinated and are therefore as infectious (36)35. Acharya, C. B., Schrom, J., Mitchell, A. M., Coil, D. A., Marquez, C., Rojas, S., … & Havlir, D. (2021). No significant difference in viral load between vaccinated and unvaccinated, asymptomatic and symptomatic groups infected with … Click for full citation (37)36. Riemersma, K. K., Grogan, B. E., Kita-Yarbro, A., Jeppson, G. E., O’Connor, D. H., Friedrich, T. C., & Grande, K. M. (2021). Vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals have similar viral loads in communities with a high prevalence of the … Click for full citation
Brown et al. (2021) and Servelitta et al (2021) suggested that vaccinated people with symptomatic infection by variants, such as Delta, are as infectious as symptomatic unvaccinated cases and will contribute to the spread of COVID even in highly vaccinated communities (38)37. Brown C.M., Vostok J., Johnson H., Burns, M., Gharpure, R., Sami, S., Sabo, R.T., Hall, N., Foreman, A., Schubert, P.L., Gallagher, G.R., Fink, T., Madoff, L.C., Gabriel, S.B.,MacInnis, B., Park, D.J., Siddle, K.J., Harik, V., Arvidson, D … Click for full citation (39)38. Servellita, V., Morris, M. K., Sotomayor-Gonzalez, A., Gliwa, A. S., Torres, E., Brazer, N., … & Chiu, C. Y. (2022). Predominance of antibody-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants in vaccine breakthrough cases from the San Francisco Bay Area, … Click for full citation.
A study from the US found that increases in COVID 19 cases are unrelated to levels of COVID-19 vaccination across 68 countries and 2,947 counties in the United States.
- On the contrary, it seems that countries with higher vaccination rates have also higher caseloads.
- It was shown that the median of new COVID-19 cases per 100,000 people was largely similar to the percent of the fully vaccinated population (40) 39. Subramanian, S. V., & Kumar, A. (2021). Increases in COVID-19 are unrelated to levels of vaccination across 68 countries and 2947 counties in the United States. European journal of epidemiology, 36(12), 1237-1240. .
Multiple recent studies have indicated that the vaccinated are more likely to be infected with Omicron than the unvaccinated.
- A study by Kirsch (2021) from Denmark suggests that people who received the mRNA vaccines are up to eight times more likely to develop Omicron than those who did not(41) 40. Kirsch, S. (2021) “New Studies Show that the COVID Vaccines Damage your Immune System, Likely Permanently,” Steve Kirsch’s Newsletter, Dec. 24, 2021, https://stevekirsch.substack.com/p/new-stu-dy-shows-vaccines-must-be. . This and a later study by
- Kirsch (2022a) conclude that the more one vaccinates, the more one becomes susceptible to COVID-19 infection (42) 41. Kirsch, S. (2022a). “Pfizer CEO says Two Covid Vaccine Doses Aren’t Enough for Omicron,” Steve Kirsch’s Newsletter Jan. 10, 2022, https://stevekirsch.subs-tack.com/p/pfizer-ceo-saystwo-covid-vaccine. .
Related Posts:
- 89.7% Cases Occurred Among The Fully Vaccinated
- Vaxxed have lower immune function & Boosters ineffective
- New Studies show C19 Vax are duds – negative benefit with useless & risky booster recommendations
- [Rant] More Vaccinated Than Unvaccinated Deaths In Australia
- MRNA Vaccines Cause Immune Suppression (Paper – Jan 2022)
This has to be seen in context with the small risk of dying from COVID-19.
- A recent peer-reviewed review paper by one of the world’s most cited and respected scientist, Professor John Ioannidis of Stanford University notes an infection fatality rate (IFR) for Covid of 0.00-0.57% (0.05% for under 70s), far lower than originally feared and no different to severe influenza (43) 42. 36. Ioannidis, J. P. (2021). Infection fatality rate of COVID-19 inferred from seroprevalence data. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 99(1), 19. .
- The chances of someone under 50 years old with symptoms dying from COVID-19 is 0.05%.
- The chances of someone under 18 years old dying from COVID is near 0%.
- Those that die usually have severe underlying medical conditions. It is estimated that children are seven times more at risk to die from influenza than from COVID-19.
A worldwide Bayesian causal Impact analysis suggests that COVID-19 gene therapy (mRNA vaccine) causes more COVID-19 cases per million and more non-Covid deaths per million than are associated with COVID-19 (44) 43. Beattie, K.A. (2021) Worldwide Bayesian Causal Impact Analysis of Vaccine Administration on Deaths and Cases Associated with COVID-19: A BigData Analysis of 145 Countries. Department of Political Science University of Alberta Alberta, Canada. .
An abundance of studies has shown that the mRNA vaccines are neither safe nor effective, but outright dangerous.
- Never in vaccine history have we seen 1011 case studies showing side effects of a vaccine (https://www.saveusnow.org.uk/covid-vaccine-scientific-proof-lethal).
- Most of these side effects have not been listed in any of the vaccine brochures or on the Australian Government websites.
- Knowing that the mRNA vaccine can be found in nearly all organs including the brain the involvement of so many organs and tissues is not surprising.
- The explanation for multiple disorders and multiple affected organs post-vaccination is the toxicity of the S1 subunit of the spike protein which creates similar symptoms as the viral disease.
- Additionally, the lipid nanoparticles alone cause inflammation and vascular damage (45) 65. Psichogiou, M., Karabinis, A., Poulakou, G., Antoniadou, A., Kotanidou, A., Degiannis, D., … & Hatzakis, A. (2021). Comparative immunogenicity of BNT162B2 mRNA vaccine with natural covid-19 infection. medRxiv. .
- The explanation for multiple disorders and multiple affected organs post-vaccination is the toxicity of the S1 subunit of the spike protein which creates similar symptoms as the viral disease.
- Knowing that the mRNA vaccine can be found in nearly all organs including the brain the involvement of so many organs and tissues is not surprising.
The Covid-19 Vaccine Monitor, an interim study report for cohort event monitoring of vaccinated persons in the EU, published on June 9, 2022 concludes that across all sites 0.2-0.3% of participants reported at least one serious adverse reaction after receiving the first and/or second dose, and similar numbers are reported after the first booster. (https://zenodo.org/record/6629551)
COVID-19 vaccines cause more side effects than any other vaccine, a fact that is attributed to its interactions with the immune system.
We are now hearing that the EU issued a warning that taking the boosters may cause adverse effects to the immune system and may not be warranted (46) 44. Reuters, “EU Drug Regulator Expresses Doubt on Need for Fourth Booster Dose,” Jan. 11, 2022, https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/eu-drug-regulator-saysmore-data–needed-impact-omicron-vaccines-2022-01-11/. .
A top Israeli immunologist has called on the leaders at the Israeli Ministry of Health to admit that the mass vaccination campaign has failed in Israel (47)45. Kirsch, S. (2022b). “Top Israeli Immunologist Criticizes Pandemic Response in Open Letter,” Jan 13, 2022, Steve Kirsch’s Newsletter, … Click for full citation.
The vaccine is in trial phase and has been linked to not only instant side effects but also short to medium-term side effects.
- Thorp et al. (2022) highlighted just a few of these side effects, such as miscarriage, foetal death and malformation, chronic autoimmune disease, permanent immune deficiency syndrome, chronic permanent CNS diseases and chronic cognitive disorders, seizure disorders and neonatal/infant cancers;
- and this only refers to foetuses and infants (48) 46. Thorp, J.A., Renz, T., Northrup, C., et al. (2022). Patient betrayal: The Corruption of healthcare, informed consent and the physician – patient relationship. 0. https://www.doi.org/10.46766/tjegms. .
Pfizer’s documents show lipid nanoparticles with their mRNA cargo being distributed throughout the entire body and passing through the blood brain, placental and foetal blood brain barriers and concentrate in the ovaries.
From US life insurance reports we know that the all-cause death rates were up 40% in ages 18-64 years by the end of Q3 2021, and according to life insurance companies there are 100,000 excess deaths per month in the US in all age groups, which cannot be attributed to COVID-19 alone [46].
In a recently published study by Doshi et al from August (49)47. Doshi, P. 2020. Covid-19: Do many people have pre-existing immunity? 17 September 2020 BMJ 2020; 370 doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m3563 **** I believe the authors mis-referenced the study, I believe the study they meant to reference was this … Click for full citation, the authors looked for serious adverse events (SAE) and adverse events of special interest (AESI) in the randomized phase III trials of both Pfizer and Moderna.
- Because both companies began unblinding study participants and offering them the vaccines only weeks after the emergency use authorization was granted by the FDA, the interim datasets from the time point of the EUA was used.
- By looking in depth at the total number of SAE instead of only the number of participants reporting one or more SAE, they found that the Pfizer injection was associated with a 36% higher risk of SAE in the vaccine versus the placebo group, while the Moderna vaccine was associated with a 6% increase of SAE in the vaccine group.
- They concluded after a simple risk-benefit analysis using the companies’ own data, that for both Pfizer and Moderna excess risk of serious AESI exceeded the benefit of reduction in Covid-19 hospitalizations.
- They finish with a request for full transparency of the Covid-19 vaccine clinical trial data which to this day are inaccessible.
- They concluded after a simple risk-benefit analysis using the companies’ own data, that for both Pfizer and Moderna excess risk of serious AESI exceeded the benefit of reduction in Covid-19 hospitalizations.
In a study by Shimabukuro et al. following 3,958 pregnant participants in the v-safe pregnancy registry only 827 (20.89%) women enrolled in the study completed pregnancy.
- In the v-safe table the number of pregnant women registered as pregnant was 30,887 and the number registered as pregnant after vaccination with either Moderna or Pfizer vaccine was 4,804, which suggests loss of pregnancy and stillbirths in 84.45% of the pregnant women. (50) 48. Shimabukuro, T. T., Kim, S. Y., Myers, T. R., Moro, P. L Oduyebo, T., Panagiotakopoulos, L., … & Meaney-Delman, D. M. (2021). Preliminary findings of mRNA Covid-19 vaccine safety in pregnant persons. New England Journal of Medicine.
Pregnancy and Vaccination
- Some concerns about vaccinating pregnant women were voiced by Anand and Stahel (51) 83. Anand, P., & Stahel, V. P. (2021). The safety of Covid-19 mRNA vaccines: A review. Patient safety in surgery, 15(1), 1-9. .
- Walsh et al. (52)89. Walsh, E.E., Frenck, R.W., Falsey, A.R. Jr., Kitchin, N., Absalon, J., Gurtman, A., Lockhart, S., Neuzil, K., Mulligan, M.J., Bailey, R. (2020). Safety and immunogenicity of two RNA-based Covid–19 vaccine candidates. New England Journal of … Click for full citation. reported that the results of the Pfizer vaccine demonstrate a broad immune response to vaccination with stimulation of neutralizing antibody responses, stimulation of CD4+ cells and growth of effector memory CD8+T cells in men and women.
- Anand and Stahel (53) 83. Anand, P., & Stahel, V. P. (2021). The safety of Covid-19 mRNA vaccines: A review. Patient safety in surgery, 15(1), 1-9. hypothesised that one could assume this would also happen in pregnant women.
- This would not be favourable for a perinatal outcome and might lead to preterm birth and fetal loss, as a good outcome relies on amplifcation of helper T cell type 2 and regulatory T cell activity coupled with decreased Th1 response (54) 90. Saito, S., Nakashima, A., Shima, T., & Ito, M. (2010). Th1/ Th2/Th17 and regulatory T?cell paradigm in pregnancy. American journal of reproductive immunology, 63(6), 601- 610. .
- Evidence has suggested that mothers with variant CD4+ T cell responses give birth to babies that may suffer enduring adverse consequences (55)91. Helmo, F. R., Alves, E. A. R., Moreira, R. A. D. A., Severino, V. O., Rocha, L. P., Monteiro, M. L. G. D. R., … & Corrêa, R. R. M. (2018). Intrauterine infection, immune system and premature birth. The journal of maternal-fetal & … Click for full citation.
In a study concentrating on the second booster dose by Regev-Yochay et al. (2022) breakthrough infections were shown to be common, mostly very mild, but with high viral loads (56) 49. Regev-Yochay, G., Gonen, T., Gilboa, M., Mandelboim, M., Indenbaum, V., Amit, S., … & Lustig, Y. (2022). Efficacy of a fourth dose of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine against omicron. New England Journal of Medicine, 386(14), 1377-1380. .
The vaccine efficacy against infection was as low as 30% for BNT162b2 (Pfizer) and 11% for mRNA1273 (Moderna) with local and systemic adverse reactions reported for 80% of BNT162b2 recipients and 40% of mRNA1273 (57) 50. Regev-Yochay, G., Gonen, T., Gilboa, M., Mandelboim, M., Indenbaum, V., Amit, S., … & Lustig, Y. 4th Dose COVID mRNA Vaccines’ Immunogenicity & Efficacy Against Omicron VOC (preprint). .
- Children under 18 are 51 times more likely to die from the mRNA vaccines than from COVID-19 if unvaccinated.
- Young adults in the age range of 18 to 29 are eight times more likely to die from vaccination than from COVID-19.
- Adults from 30 to 39 are seven times more likely to die from vaccination.
- Ages 40 to 49 are five times more likely to die after vaccination.
- People in the group aged 50 to 59 are still twice as likely to die after vaccination than after COVID-19.
- Only when over 60 years of age is the chance of death equal for both causes.
- Even when over 80 years old the likelihood of dying from Covid inoculation is just 0.13% lower than the risk of dying from the infection.
- The authors concluded that the protection from COVID-19 death falls far short of the risk of dying from the vaccine for people below 50 years old (58) 51. Dopp, K, Seneff, S. (2022). COVID-19 and All-Cause Mortality Data by Age Group Reveals Risk of COVID Vaccine-Induced Fatality is Equal to or Greater than the Risk of a COVID death for all Age Groups Under 80 Years Oldas 2022: 1-21. .
Jab Deaths 5x higher in most vulnerable
According to Kostoff (59) 52. Kostoff, R.N., Calina, D., Kanduc, D., Briggs, M.B., Vlachoyiannopoulos, P., Svistunov, A.A., Tsatsakis, A.. 2021. Why are we vaccinating children against COVID-19? Toxicology Reports. 8, 1665-1684. the number of deaths attributable to each inoculation is five times higher in the most vulnerable 65+ demographic than deaths attributable to COVID–19.
- With decreasing age, the risk of death from COVID-19 decreases drastically.
- Combined with the longer-term effects of the inoculations, most of which are still unknown, this increases the risk-benefit ratio, perhaps substantially, in the lower age groups.
What needs to be further emphasised is that the majority of deaths with and from COVID- 19 occur in the elderly with multiple comorbidities and generally weaker immune systems.
- Yet they are vaccinated with an injection that amplifies underlying disorders and is dependent on a strong immune response.
- Ironically, the survival of many of those patients is probably due to their immune system not being able to mount a significant response to the induced spike protein production.
A study looking at the length of protection over time indicated that immunity against the delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 waned in all age groups a few months after receiving the second dose of the vaccine (60)53. Goldberg, Y., Mandel, M., Bar-On, Y.M., Bodenheimer, O.,Freedman, L., Haas, E.J., Milo, R., Alroy-Preis, S., Ash, N., Huppert, A. (2021). Waning Immunity after the BNT162b2 Vaccine in Israel. New England Journal of Medicine, 385(24):e85. doi: … Click for full citation.
Another study found that antibody titres increased significantly at five weeks after the first vaccination but decreased rapidly at four months after the second injection. This significant decrease was independent of gender or age (61) 54. Jo, D.-H., Minn, D., Lim, J., Lee, K.-D., Kang, Y.-M., Choe, K.-W., Kim, K.-N. (2021). Rapidly declining SARSCoV-2 antibody titers within 4 months after BNT162b2 vaccination. Vaccines, 9, 1145. .
The fact that immunity after vaccinations seems to wane over time has been reported by other researchers who also found that antibody titres are decreasing by up to 40% each months (62)55. Israel, A., Shenhar, Y., Green, I., Merzon, E., Golan- Cohen, A., Schäffer, A.A., Ruppin, E., Vinke,r S, Magen, E. (2021). Large-scale study of antibody titer decay following BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine or SARS-CoV-2 infection. medRxiv [Preprint]. … Click for full citation with no detectable antibody levels recorded in 16.1% of the subjects in one study within six months.
Therefore, booster vaccinations were recommended (63)56. Binkin, N.J., Laurent, L.C., Pride, D., Longhurst, C.A., Abeles, S.R., Torriani, F.J. (2021). Resurgence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in highly vaccinated health system workforce. The New England Journal of Medicine. … Click for full citation.
Another study found that decrease in neutralising antibody titres to alpha, beta, gamma and delta variants was not significantly different between the different vaccines. They used modelling and predicted below 50% protection against symptomatic infection within the first year, also urgently recommending booster shots (64)57. Cromer, D., Steain, M., Reynaldi, A., Schlub, T.E., Wheatley, A.K., Juno, J.A., Kent, S.J., Triccas, J.A., Khoury, D.S., Davenport, M,P. (2022). Neutralising antibody titres as predictors of protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants and the impact … Click for full citation.
Scientists agree though, that introducing a booster too early and too frequently carries increased risks especially for vaccines that have immune-mediated side-effects, such as myocarditis, Guillaine-Barre syndrome and thrombosis (65) 58. Krause P.R., Fleming, T.R.., Peto, R., Longini, I., Figueroa, J.P., Sterne, J.A.C., et al. (2021). Considerations in boosting COVID-19 vaccine immune responses. The Lancet 398, 1377 -10380. .
Lui et al. (66) 59. Lui, L., Luo, Y., Chu, H. et al. (2021) Striking antibody evasion manifested by the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-03826-3(2021). specifically looked at protection against Omicron and concluded that the Omicron variant of COVID-19 was remarkedly resistant to neutralization by serum from individuals vaccinated with one of the four widely used COVID-19 vaccines. Serum from persons vaccinated and boosted with mRNA-based vaccine was also showing substantially diminished neutralization of Omicron.
A study investigated the neutralizing antibody titres against the reference strain WA1/2020 and omicron subvariants BA.1, BA.2, BA.2.12.1 and BA.4 or BA.5. in participants that had been double vaccinated and boosted with the Pfizer mRNA vaccine versus participants that had been vaccinated (bar one) and infected with the BA.1 or BA.2 variant of omicron on average 29 days prior. Their conclusion was that compared to the reference strain neutralising antibody titres to the Omicron variants were substantially decreased in both groups (6.4, 7.0 and 14.1 times (vaccinated) and 6.4, 5.8 and 9.6 times (infected) lower against BA.1, BA.2, BA.2.12.1 respectively and 21.0 (vaccinate) and 18.7 (infected) times lower against BA.4 or BA.5), suggesting that the later variants increasingly escape neutralizing antibodies (67)60. Hachmann, N. P., Miller, J., Collier, A. R. Y., Ventura, J. D., Yu, J., Rowe, M., … & Barouch, D. H. (2022). Neutralization escape by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA. 2.12. 1, BA. 4, and BA. 5. New England Journal of Medicine, 387(1), … Click for full citation.
Even a fourth shot of a Covid-19 vaccine is “not good enough” to prevent Omicron, according to a preliminary study in Israel.
- Sheba Hospital tested a fourth shot given to more than 270 medical workers, with 154 getting the Pfizer jab and 120 receiving Moderna.
- The researchers found that both groups showed a “slight” increase in antibodies – but not sufficient to prevent Omicron.
- Disturbingly, the vaccinated infected health care workers had relatively high viral loads, which suggests that they were infectious [49].
- The researchers found that both groups showed a “slight” increase in antibodies – but not sufficient to prevent Omicron.
In a letter to the editor Yamamoto (2022) sums up the literature pointing to the fact that 8 months after being vaccinated twice the immune functions are less than those of an unvaccinated person according to a study by Nordstroem et al (2022) (68) 61. Yamamoto, K. (2022). Adverse effects of COVID-19 vaccines and measures to prevent them. Virology Journal, 19(1), 1-3. .
Booster shots can impair immunity due to a variety of factors leading to the recommendation to discontinue further booster shoots.
- A paper by John Gibson from the University of Waikato looked at the excess death rate in New Zealand and found that rising excess mortality was closely related to the booster rollout.
- The author calculated 16 excess deaths for each 100,000 booster doses (https://repec.its.waikato.ac.nz/wai/econwp/2211.pdf).
According to the Health NSW government site the data obtained in 14 days until 16th of July 2022 continues to show the trend of worsening effects after the booster shots (https://www.health.nsw.gov.au/Infectious/covid-19/Documents/weekly-covid-overview-2-22-716.pdf)
It is truly disturbing that treatments successfully being used to treat COVID-19 patients, have not been investigated in Australia.
- These treatments are mainly based on vitamins, zinc and zinc ionophores, such as ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine.
- The recommendation is to treat as early as possible.
- Scientific papers support the use of ivermectin according to Bryant et al. (69)62. Bryant, A., Lawrie, T. A., Dowswell, T., Fordham, E. J., Mitchell, S., Hill, S. R., & Tham, T. C. (2021). Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to … Click for full citation.
- They found moderate to strong evidence that ivermectin can reduce COVID-19 deaths while being safe and inexpensive.
- The same was found for hydroxychloroquine in a review by McCullough et al, which also stated that a reduction of mortality strongly depends on an early start of the treatment.
- Hydroxychloroquine has been registered in the US since 1955 and has a well-characterized safety profile (70)63. Bruno, R., Mccullough, P. A., Vila, T. F. I., Henrion-Caude, A., Garcia-Gasca, T., Zaitzeva, G. P., … & Acevedo-Whitehouse, K. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 mass vaccination: Urgent questions on vaccine safety that demand answers from international … Click for full citation.
Yet here in Australia the recommendation is to isolate and monitor yourself.
- Only if you have difficulty breathing, experience loss of speech or mobility, confusion or chest pain should you contact the health care provider.
- Additionally, the government strongly advises not to use the following treatment for COVID-19 off label: Ivermectin, doxycycline, zinc and hydroxychloroquine (https://www.health.gov.au/health-alerts/covid-19/treatments).
The TGA provisionally approved the first oral treatments in January 2022 for Australia, Lagevrio® (molnupiravir) and Paxlovid®(nirmatrelvir + ritonavir) and recommend that both treatments should be started as soon as possible after diagnosis of COVID-19 (https://www.health.gov.au/health-alerts/covid-19/treatments/oral).
- The TGA also accepted – similar to the agreement for the provisionally approved vaccines – rolling data for COVID-19 treatments, to enable early evaluation of data as it comes to hand (https://www.tga.gov.au/apm-summary/lagevrio).
- In other words, both drugs have been provisionally approved on the basis of short-term efficacy and safety data and permanent approval depends on the efficacy and safety data from ongoing clinical trials and postmarketing assessment. (https://www.ebs.tga.gov.au/ebs/picmi/picmirepository.nsf/pdf?OpenAgent&id=CP-2022-PI-01049-1)
- Therefore, these treatments are still in trial phase and all patients treated with them are trial participants.
- Paxlovid has listed numerous potential complex and serious drug-drug interactions against its registration which could result in severe or life-threatening side effects (https://www1.racgp.org.au/newsgp/clinical/what-gpsneed-to-know-about-the-new-covid-antivira).
- Therefore, these treatments are still in trial phase and all patients treated with them are trial participants.
- In other words, both drugs have been provisionally approved on the basis of short-term efficacy and safety data and permanent approval depends on the efficacy and safety data from ongoing clinical trials and postmarketing assessment. (https://www.ebs.tga.gov.au/ebs/picmi/picmirepository.nsf/pdf?OpenAgent&id=CP-2022-PI-01049-1)
Just to name a few short-term side effects: Death, Cardiac disorders such as Myocarditis, Blood and lymphatic system disorders, such as blood clots, thrombocytopenia, low platelet count, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, capillary leakage syndrome, Congenital and genetic disorders, Eye disorders, Immune disorders, Muscular, skeletal and connective tissue disorders, Cancerous tumours, Nervous system disorders, Pregnancy and perinatal conditions, Guillain-Barre syndrome and the list goes on.
Pfizer’s documents demonstrate lipid nanoparticles with their mRNA cargo being distributed to the entire body and pass through the blood brain, placental and foetal blood brain barriers and concentrate in the ovaries. The vaccine is in trial phase and has been linked to not only instant but also long-term side effects.
Thorp et al. (71) 46. Thorp, J.A., Renz, T., Northrup, C., et al. (2022). Patient betrayal: The Corruption of healthcare, informed consent and the physician – patient relationship. 0. https://www.doi.org/10.46766/tjegms. highlighted just a few of the side effects, such as miscarriage, foetal death and malformation, chronic autoimmune disease, permanent immune deficiency syndrome, chronic
permanent CNS diseases and chronic cognitive disorders, seizures and neonatal/infant cancers; and this is only with regard to foetuses and infants.
The data from NSW showed clearly that COVID injections were correlated with increases in hospitalization and ICU admissions and indicate a relation to death with COVID injections.
- The increase in hospitalisation, ICU admissions and deaths is very pronounced after the third injection although only 69% of the population took the booster shot versus 95% taking the initial series.
The Australian Bureau of statistics has just released the national death rate for March 20, 2021 up until 31 March 2022 (registered by 31 May 2022) as 44,331, which according to their own statement lies 6,609 (17.5%) above the historical average.
- These extra deaths cannot be explained by COVID alone which is responsible for less than half of the excess deaths in the first 4 months of 2022 in Australia.
- Cancer, diabetes and neurodegenerative diseases are all above the baseline in this time frame (https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/health/causes-death/provisional-mortality-statistics/latest-release).
We get an insight into what is really going on in England where the government released COVID related death data (if the death certificate mentioned COVID) and all other death data sorted by vaccination status.
- The overall death rate for the unvaccinated was 17% while for the vaccinated it was 83%.
- The trend seems to be an ever increasing all causes death rate with added vaccinations without getting any protection from additional injections.
Unexplained deaths in Germany have been shown to be the consequence of mRNA vaccines causing an autoimmune response of CD8 T killer lymphocytes in all organ systems throughout the body.
- Dr Sucharit and Dr Burkhardt stated that the mRNA vaccine is killing the young and the old (https://doctors4covidethics.org/on-covid-vaccines-why-they-cannot-work-and-irrefutableevidence-of-their-causative-role-in-deaths-after-vaccination/).
According to the VAERS database over 22,000 deaths have been associated with the COVID-19 vaccine.
- This is particularly alarming as according to the VAERS website adverse events could be between 10 and 100, so the actual number of deaths is likely much higher and could be over a million.
From large insurance companies in the US we know that the allcause death rates are up 40% in ages 18-64 years and there are 100,000 excess deaths per month in the US across all age groups, which cannot be attributed to COVID-19 alone.
- However, caution has to be taken in interpreting these data as deaths due to suicides and delayed hospital treatment are not taken into consideration.
- Nevertheless, the trend seems to be the same and should raise alarm.
A study by Gat et al. on semen of male semen donors revealed a transient decrease in semen concentration and a reduction in the total motile count (TMC) after COVID-19 vaccination (72) 64. Gat, I., Kedem, A., Dviri, M., Umanski, A., Levi, M., Hourvitz, A., & Baum, M. (2022). Covid?19 vaccination BNT162b2 temporarily impairs semen concentration and total motile count among semen donors. Andrology, 10(6), 1016-1022. .
Spike proteins enter the circulation when the cell they were attached to is destroyed by the immune system.
- The freely circulating spike proteins attach to any cell that expresses ACE2 receptors, explaining the multitude of sites where disorders occur (73) 75. Salamanna, F., Maglio, M., Landini, M.P., Fini, M. (2020). Body Localization of ACE-2: On the Trail of the Keyhole of SARS-CoV-2. Frontiers in Medicine, 7, https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2020.594495 .
- Not only does spike protein produces unwanted side effects, but mRNA and nanoparticles do as well.
- Seneff et al enumerated Covid-19 vaccine effects on the innate immune system, importantly a decrease of type I interferon signalling, as well as disturbances in the regulation of protein synthesis affecting the formation of immune cells and the apoptosis of tumor cells. (74) 15. Seneff, S., Nigh, G., Kyriakopoulos, A. M., & McCullough, P. A. (2022). Innate immune suppression by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinations: The role of G-quadruplexes, exosomes, and MicroRNAs. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 164, 113008. .
- The suppression of the interferon response by the mRNA vaccines alone can lead to a wide variety of disorders, such as reactivation of viral infections and reduce the immune system’s ability to not only fight disease but to keep tumors and autoimmune reactions suppressed (75) 73. Passegu, E., Ernst, P.A. (2009). IFN-alpha wakes up sleeping hematopoietic stem cells Natural Medicine, 15 (6), Article 612613, 10.1038/nm0609-612 .
- A case report by Glas et al from (76)74. Glas, M., Smola, S., Pfuhl, T., Pokorny, J., Bohle, R.M., Bücker, A., Kamradt J., Volk T. Fatal Multiorgan Failure Associated with Disseminated Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Infection: A Case Report. Case Reports in Critical Care, Volume 2012 doi: … Click for full citation illustrates the effects of a disseminated viral infection on an immune-suppressed patient:
- In this instance fatal multiorgan failure associated with disseminated Herpes simplex virus-1 infection.
- Considering that reactivation and spread of dormant viral infections including Herpes simplex and Herpes zoster are listed as side effects from both mRNA injections as well as the Astra Zeneca vaccine, it is maybe not surprising that pathology reports by Dr Sucharit and Dr Burkhardt (2021) show multiorgan failure as cause of death in several cases of post-vaccine deaths.
- In this instance fatal multiorgan failure associated with disseminated Herpes simplex virus-1 infection.
Another method of viral spread that escapes the immune system is the formation of syncytia which can be induced by the spike protein itself.
- Heterotypic cell-in-cell structures with lymphocytes inside multinucleate syncytia are prevalent in the lung tissues of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients.
- This membrane fusion is dictated by a bi-arginine motif within the polybasic S1/S2 cleavage site leading to the formation of multinucleate syncytia.
- Host metalloproteases (ADAM-17 and ADAM-10) promote such spike protein-mediated lung cell fusion (77) 76. Jocher, G., Grass, V., Tschirner, S. K., Riepler, L., Breimann, S., Kaya, T., … & Lichtenthaler, S. F. (2022). ADAM10 and ADAM17 promote SARS?CoV?2 cell entry and spike proteinmediated lung cell fusion. EMBO reports, 23(6), e54305. (78) 77. Pepe, A., Pietropaoli, S., Vos, M., Barba-Spaeth, G., & Zurzolo, C. (2022). Tunneling nanotubes provide a route for SARS-CoV-2 spreading. Science advances, 8(29), eabo0171.
- This membrane fusion is dictated by a bi-arginine motif within the polybasic S1/S2 cleavage site leading to the formation of multinucleate syncytia.
Pepe et al (2022) (79) 77. Pepe, A., Pietropaoli, S., Vos, M., Barba-Spaeth, G., & Zurzolo, C. (2022). Tunneling nanotubes provide a route for SARS-CoV-2 spreading. Science advances, 8(29), eabo0171. showed furthermore that the formation of tunneling nanotubes can be induced by Covid-19 in a so far undisclosed way and used to transport viral particles or indeed viral components like S and N proteins from infected to ordinarily non-permissive cells, e.g. neuronal cells.
Not enough time has passed since administration of the first injections to know what the long-term effects might be.
Long-term risks of vaccination as predicted by scientists, many already validated by scientists and doctors: (80) 78. Kelleni, M. T. (2021). SARS CoV-2 Vaccination Autoimmunity, Antibody Dependent Covid-19 Enhancement and Other Potential Risks: Beneath the Tip of the Iceberg. International Journal of Pulmonary & Respiratory Sciences, 5(2), 555658. (81) 79. Lyons-Weiler, J. (2020). Pathogenic priming likely contributes to serious and critical illness and mortality in COVID-19 via autoimmunity. Journal of translational autoimmunity, 3, 100051. (82) 80. Hasan, A., Al-Mulla, M. R., Abubaker, J., & Al-Mulla, F. (2021). Early insight into antibody-dependent enhancement after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 17(11), 4121-4125. (83) 81. Classen, J. B. (2021). COVID-19 RNA based vaccines and the risk of prion disease. Microbiol Infect Dis, 5(1), 1-3. (84) 82. Idrees, D., & Kumar, V. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interactions with amyloidogenic proteins: Potential clues to neurodegeneration. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 554, 94-98. (85) 83. Anand, P., & Stahel, V. P. (2021). The safety of Covid-19 mRNA vaccines: A review. Patient safety in surgery, 15(1), 1-9. (86)84. Aldén, M., Olofsson Falla, F., Yang, D., Barghouth, M., Luan, C., Rasmussen, M., & De Marinis, Y. (2022). Intracellular reverse transcription of Pfizer BioNTech COVID-19 mRNA vaccine BNT162b2 in vitro in human liver cell line. Current … Click for full citation
- Vaccine-induced autoimmunity,
- pathogenic priming,
- multisystem inflammatory disease and autoimmunity,
- antibody dependent enhancement (ADE),
- activation of latent viral infections,
- neurodegeneration and prion disease,
- increased thrombosis, cardiomyopathy and other vascular events following vaccination,
- babies suffering enduring adverse consequences,
- mRNA reverse transcribing intracellularly into the DNA
- and death due to autoimmune disease long after vaccination
Autoimmune Disease
A study by Lyons-Weiler (87) 79. Lyons-Weiler, J. (2020). Pathogenic priming likely contributes to serious and critical illness and mortality in COVID-19 via autoimmunity. Journal of translational autoimmunity, 3, 100051. revealed that over 1/3 of SARS CoV-2 proteins, including the spike protein show problematic homology to key proteins in the human adaptive immune system which might lead to autoimmune reactions against these proteins.
Kelleni (88) 78. Kelleni, M. T. (2021). SARS CoV-2 Vaccination Autoimmunity, Antibody Dependent Covid-19 Enhancement and Other Potential Risks: Beneath the Tip of the Iceberg. International Journal of Pulmonary & Respiratory Sciences, 5(2), 555658. reports on the potential risk of the vaccine to induce auto-immune diseases such as thrombocytopenia, myocarditis and immune induced thrombosis and thromboembolism which
can have fatal outcomes and might be behind some of the post vaccination reports on sudden deaths.
Antibody Dependent Enhancement (ADE)
Hasan et al. (89) 80. Hasan, A., Al-Mulla, M. R., Abubaker, J., & Al-Mulla, F. (2021). Early insight into antibody-dependent enhancement after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 17(11), 4121-4125. analysed data from the National Health Service published by Public Health England and showed that the death
rate due to the Delta variant infection was eight times higher in fully vaccinated than in unvaccinated infected people.
- The authors suggest that in a subset of individuals the pre-existing anti-S-IgG titre induced by vaccination may be sub-neutralizing and leading to accelerated infectivity via ADE, which is displayed as higher death rates.
Prion Disease
The potential risk factors of the mRNA or vector DNA vaccine are protein sequences that can induce TDP-43 and FUS to aggregate into prion configuration, which might lead to neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimers [85].
- The spike protein encoded by the mRNA binds to the ACE2 receptor which releases zinc molecules.
- Zinc also causes TDP-43 to transform into a pathological prion (90) 81. Classen, J. B. (2021). COVID-19 RNA based vaccines and the risk of prion disease. Microbiol Infect Dis, 5(1), 1-3. .
- The link with neurodegenerative disease is the ability of the spike protein to interact with the heparin binding amyloid forming proteins.
- A study indicated that the S1 protein forms a stable bond with the aggregation-prone proteins, which might initiate aggregation of brain proteins and thereby accelerate neurodegeneration (91) 82. Idrees, D., & Kumar, V. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interactions with amyloidogenic proteins: Potential clues to neurodegeneration. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 554, 94-98. .
- Finisterer and Scorza (92) 86. Finisterer J., Scorza, F.A. 2021. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are not free of neurological side effects. Acta Neurology Scandinavia 144, 109-110. doi: 10.1111/ane.13451 further stated that SARS-CoV-2 vaccines trigger neurological adverse reactions and both mild and severe neurological side effects have been occasionally reported.
- Studies support the theory that the onset and progression of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer and Parkinson disease, including TDP-43 proteinopathy, are associated with propagation of protein aggregates between neuronal cells.
- These speculations are supported by a case report of prion disease due to vaccination from Turkey (93) 87. Kuvandik, A., Özcan, E., Serin, S., Sungurtekin, H. (2021). Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease After the COVID-19 Vaccination. Turkish Journal of Intensive Care. DOI: 10.4274/tybd.galenos.2021.91885. (94) 88. Serin, S., & Sungurtekin, H. (2021). Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease After the COVID-19 Vaccination.
Thrombosis, Capillary Leakage Syndrome and Myocarditis
Scientific studies have raised serious concerns about the safety of AstraZeneca after reports of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and a variety of other thrombotic events the AstraZeneca vaccination with studies reporting such events in medical journals.
- Kircheis (95) 22. Kircheis, R. 2021. Coagulopathies after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 may be derived from a combined effect of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and adenovirus vector-triggered signaling pathways. International Journal of Molecular Science, . reported that other serious conditions have been reported for COVID vaccines such as capillary leakage syndrome (AstraZeneca) and coronary myocarditis (Pfizer).
Side Effects Acknowledged but Played Down as Extremely Small Risk
The TGA report in Australia on a weekly basis and the report of the 2nd of September 2021 mentioned nine more blood clots and low platelet counts, confirmed as probably Thrombocytopenia syndrome linked to the AstraZeneca vaccine with two connected deaths during that week, one from Queensland and one from NSW.
- An assessment of the 125 cases of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) showed that women in the younger age groups were slightly more likely to develop TTS in more unusual places such as brain and abdomen with more serious outcomes projected (TGA).
Another rare side effect is Guillian-Barre syndrome (GBS), which affects the nerves.
- Up to the 29 August 99 reports of GBS after vaccination have been received.
Further 61 reports of immune thrombocytopenia were lodged after AstraZeneca vaccination.
For the Pfzer vaccine the TGA reports 293 instances of suspected myocarditis and/or pericarditis following vaccination to the 29 August 2021.
- Nine of these reports were from children 16 to 17 years of age.
A study concluded that observations of increased thrombosis, cardiomyopathy and other vascular events following vaccination might be caused by the mRNA vaccines dramatically increasing inflammation of the endothelium and T cell infiltration of cardiac muscle (96) 92. Gundry, S. R. (2021). MRNA COVID vaccines dramatically increase endothelial inflammatory markers and ACS risk as measured by the PULS cardiac test: A warning. Circulation. .
At a parliament enquiry by US senator Ron Johnson lawyer Thomas Renz presented three US military doctors, Drs. Samuel Sigoloff, Peter Chambers, and Theresa Long, whose declarations he planned to use in federal court under penalty of perjury. (https://newlifenarrabri.wordpress.com/2022/02/01/jo-nova-hugespike-in-us-military-injuries-from-covid-vaccinations/) and (https://www.ronjohnson.senate.gov/2022/2/sen-johnson-to-secretaryaustin-has-dod-seen-an-increase-in-medical-diagnoses-amongmilitary-personnel)
- These doctors revealed a 300% increase in miscarriages in the military above the five-year average in 2021 with the five-year average being 1,499 miscarriages per year while in the first 10 months of 2021 the registered miscarriages were 4,182.
- Other diseases went up in a similar fashion such as an almost 300% increase in cancer diagnoses (from a five-year average of 38,700 per year to 114,645 in the first 11 months of 2021).
- Neurological issues increased by 1000% from a baseline average of 82,000 to 863,000 in 2021.
Some other increased conditions were:
- 269% increase of myocardial infarction
- 291% increase of Bell’s palsy
- 156% increase of children’s congenital malformations of military personnel
- 471% increase of female infertility
- 467% increase of pulmonary embolisms
According to an interview in February 2022 with Julian Gillespie, who is currently fighting in court against the vaccine mandates, an evaluation of the TGA reports revealed that Australia’s average of adverse events after vaccination since 1971 up to 2020 is recorded as 2.4 death per year and up to 3,500 adverse events per annum.
- Since the rollout of the COVID vaccines there have been 755 deaths and 105,000 adverse events in a year with these figures likely to be underreported.
The question is how many deaths and side effects are we accepting as normal for vaccines and where do we draw the line to say more investigations need to be done before any further vaccines are distributed?
Never in Vaccine history have 57 leading scientists and policy experts released a report questioning the safety and efficacy of a vaccine (97)93. Bruno, R., Mccullough, P.A., Forcades, I., Vila, T. et al. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 mass vaccination: Urgent questions on vaccine safety that demand answers from international health agencies, regulatory authorities, governments and vaccine … Click for full citation.
- They not only questioned the safety of the current Covid-19 injections, but were calling for an immediate end to all vaccination.
- Many doctors and scientists around the world have voiced similar misgivings and warned of consequences due to long-term side effects.
Yet there is no discussion or even mention of studies that do not follow the narrative on safety and efficacy of Covid-19 vaccination.
In the USA, as Blaylock (98) 94. Blaylock, R. L. (2022). COVID UPDATE: What is the truth?.Surgical Neurology International, 13. states it very nicely, federal bureaucrats have forced the acceptance of special forms of care and prevention, which includes experimental mRNA vaccines (99)93. Bruno, R., Mccullough, P.A., Forcades, I., Vila, T. et al. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 mass vaccination: Urgent questions on vaccine safety that demand answers from international health agencies, regulatory authorities, governments and vaccine … Click for full citation.
Medical experts that have questioned the safety of these vaccines have been attacked and demonised, called conspiracy theorists and have been threatened to be de-registered if they go against the narrative.
Alternative treatments were prohibited and people who never practised medicine are telling experienced doctors how to do their job.
- AHPRA is doing the same here in Australia to the detriment and in ignorance of science.
When Adjunct Professor John Skerritt, who is currently the Deputy Secretary and directly responsibility for both the Therapeutic Goods Administration and the Office of Drug Control, was asked why the registration process for vaccines was shortened he wrote:
“It is nonsense to assert that vaccines typically take 10 years to licence. The standard regulatory process for vaccines is about 10-12 calendar months and in the case of COVID-19 vaccines this period was shortened by accepting data on a rolling basis, teams reviewing different parts of the dossier in parallel, working collaboratively with international regulators, and by many members of the teams working long hours” (personal e-mail communication).
One has to wonder how they propose to assess long-term side effects.
Can we really trust any pharmaceutical drug approval by the TGA after this statement?
Pfizer never planned to reveal its clinical trial data and had to be ordered by a judge in the USA to release the data to the public.
- Even then they and the FDA tried to limit the number of pages published per month which would have made the full study data public knowledge sometime in the 2070ies.
- The reason given was that some proprietary information had to be blacked out before release to the public.
Again, it is inconceivable why it would be impossible to go through the study data in a few months, when it took the FDA less than 4 weeks to give the injections emergency use authorization – unless you want to entertain the idea that the study data were never actually read and scrutinised, a frightening perspective.
*** I think there is another nefarious reason for not releasing the study data and it starts with over 1,200 dead in the first 3 months. ~ Penny
*** Authors, if you ever find this, please update your paper to reflect it was the FDA, not the CDC. ~ Penny
Citation: Conny Turni and Astrid Lefringhausen (2022) COVID-19 vaccines – An Australian Review. Journal of Clinical & Experimental Immunology. 7(3):491-508. (100) Conny Turni and Astrid Lefringhausen (2022) COVID-19 vaccines – An Australian Review. Journal of Clinical & Experimental Immunology. 7(3):491-508 21 Sep 2022 https://opastpublishers.com/open-access/covid-19-vaccines-an-australian-review.pdf
Copyright: ©2022: Conny Turni. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

Site Notifications/Chat:
- Telegram Post Updates @JourneyToABetterLife (channel)
- Telegram Chatroom @JourneyBetterLifeCHAT (say hi / share info)
- Gettr Post Updates @chesaus (like fakebook)
Videos:
References[+]
| 01 | 1. Hansen, T., Titze, U., Kulamadayil-Heidenreich, N. S. A., Glombitza, S., Tebbe, J. J., Röcken, C., & Wilkens, L. (2021). First case of postmortem study in a patient vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 107, 172-175. |
|---|---|
| 02 | 2. Ndeupen, S., Qin, Z., Jacobsen, S., Bouteau, A., Estanbouli, H., & Igyártó, B. Z. (2021). The mRNA-LNP platform’s lipid nanoparticle component used in preclinical vaccine studies is highly inflammatory. Iscience, 24(12), 103479. |
| 03 | 3. Zhou, Y., Peng, Z., Seven, E. S., & Leblanc, R. M. (2018). Crossing the blood-brain barrier with nanoparticles. Journal of controlled release, 270, 290-303. |
| 04 | 4. Wick, P., Malek, A., Manser, P., Meili, D., Maeder-Althaus,X., Diener, L., … & von Mandach, U. (2010). Barrier capacity of human placenta for nanosized materials. Environmental health perspectives, 118(3), 432-436. |
| 05 | 5. Shimazawa, R., & Ikeda, M. (2021). Potential adverse events in Japanese women who received tozinameran (BNT162b2, Pfizer-BioNTech). Journal of Pharmaceutical Policy and Practice, 14(1), 1-3. |
| 06 | 6. Karikó, K., Buckstein, M., Ni, H., & Weissman, D. (2005). Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: the impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity, 23(2), 165-175. |
| 07 | 7. Karikó, K., Muramatsu, H., Welsh, F. A., Ludwig, J., Kato, H., Akira, S., & Weissman, D. (2008). Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA yields superior nonimmunogenic vector with increased translational capacity and biological stability. Molecular therapy, 16(11), 1833-1840. |
| 08 | 8. Röltgen, K., Nielsen, S.C.A., Silv,a O., Younes, S.F. et al. (2022). Immune imprinting, breadth of variant recognition, and germinal center response in human SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. Cell, 185, 1025 – 1040. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.018 |
| 09 | 9. Biancatelli, R. M. C., Solopov, P. A., Sharlow, E. R., Lazo, J. S., Marik, P. E., & Catravas, J. D. (2021). The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunit S1 induces COVID-19-like acute lung injury in ?18-hACE2 transgenic mice and barrier dysfunction in human endothelial cells. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. |
| 10 | 10. Zhang, S., Liu, Y., Wang, X., Yang, L., Li, H., Wang, Y., … & Hu, L. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 binds platelet ACE2 to enhance thrombosis in COVID-19. Journal of hematology & oncology, 13(1), 1-22. |
| 11 | 11. Cattin-Ortolá, J., Welch, L. G., Maslen, S. L., Papa, G., James, L. C., & Munro, S. (2021). Sequences in the cytoplasmic tail of SARS-CoV-2 Spike facilitate expression at the cell surface and syncytia formation. Nature communications, 12(1), 1-11. |
| 12 | 12. Cheng, Y. W., Chao, T. L., Li, C. L., Wang, S. H., Kao, H. C., Tsai, Y. M., … & Yeh, S. H. (2021). D614G substitution of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein increases syncytium formation and virus titer via enhanced furin-mediated spike cleavage. Mbio, 12(4), e00587-21. |
| 13 | 13. Singh, N., & Singh, A. B. (2020). S2 subunit of SARS-nCoV-2 interacts with tumor suppressor protein p53 and BRCA: an in silico study. Translational Oncology, 13(10), 100814. |
| 14, 75 | 73. Passegu, E., Ernst, P.A. (2009). IFN-alpha wakes up sleeping hematopoietic stem cells Natural Medicine, 15 (6), Article 612613, 10.1038/nm0609-612 |
| 15 | 14. Liu, J., Wang, J., Xu, J., Xia, H., Wang, Y., Zhang, C., …& Liu, Z. (2021). Comprehensive investigations revealed consistent pathophysiological alterations after vaccination with COVID-19 vaccines. Cell discovery, 7(1), 1-15. |
| 16, 74 | 15. Seneff, S., Nigh, G., Kyriakopoulos, A. M., & McCullough, P. A. (2022). Innate immune suppression by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinations: The role of G-quadruplexes, exosomes, and MicroRNAs. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 164, 113008. |
| 17 | 16. Mishra, R., Banerjea, A.C. (2021) SARS-CoV-2 Spike Targets USP33-IRF9 Axis via Exosomal miR-148a to Activate Human Microglia. Frontiers in Immunology, 12. DOI=10.3389/fimmu.2021.656700 |
| 18 | 17. Reiss, K., & Bhakdi, S. (2020). Corona, False Alarm?: Facts and Figures. Chelsea Green Publishing. |
| 19 | 18. Doshi, P. (2020). Covid-19: Do many people have pre-existing immunity?. Bmj, 370. |
| 20 | 19. Ng, K. W., Faulkner, N., Cornish, G. H., Rosa, A., Harvey, R., Hussain, S., … & Kassiotis, G. (2020). Preexisting and de novo humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in humans. Science, 370(6522), 1339-1343. |
| 21 | 20. King, E. M. (2020). T-cells Are the Superstars in Fighting COVID-19. But Why are some People So Poor at Making Them?. bmj, 370. |
| 22 | 21. Phillips, N. (2021). The corona virus will become endemic. Nature, 590: 382-384. |
| 23 | 22, 10791. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910791. |
| 24 | 23. Oran, D.P., Topol, E.J. (2021). The Proportion of SARS-CoV-2 Infections That Are Asymptomatic : A Systematic Review. Annual Interntional Medicines, 174(5): 655-662. doi: 10.7326/M20-6976. |
| 25 | 24. Ivanova, E., Devlin, J., Buus, T., Koide, A., Cornelius, A., Samanovic, M., … & Koralov, S. B. (2021). Discrete immune response signature to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination versus infection. |
| 26 | 25. Seneff, S. and Nigh, G. (2021). Worse than the disease? Reviewing some possible unintended consequences of the mRNA vaccines against COVID-19. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 2, 38 – 79. |
| 27 | 26. Cardozo, T., & Veazey, R. (2021). Informed consent disclosure to vaccine trial subjects of risk of COVID-19 vaccines worsening clinical disease. International journal of clinical practice, 75(3), e13795. |
| 28 | 27. Nordström, P., Ballin, M., & Nordström, A. (2022). Risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection and COVID-19 hospitalisation in individuals with natural and hybrid immunity: a retrospective, total population cohort study in Sweden. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 22(6), 781-790. |
| 29 | 28. Nordström, P., Ballin, M., & Nordström, A. (2022). Risk of infection, hospitalisation, and death up to 9 months after a second dose of COVID-19 vaccine: a retrospective, total population cohort study in Sweden. The Lancet, 399(10327), 814-823. |
| 30 | 29. Israel, A., Shenhar, Y., Green, I., Merzon, E., Golan-Cohen, A., Schäffer, A. A., … & Magen, E. (2021). Large-scale study of antibody titer decay following BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine or SARS-CoV-2 infection. Vaccines, 10(1), 64. |
| 31 | 30. Lozano-Ojalvo, D., Camara, C., Lopez-Granados, E., Nozal, P., del Pino-Molina, L., Bravo-Gallego, L. Y., … & Ochando, J. (2021). Differential effects of the second SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine dose on T cell immunity in naive and COVID-19 recovered individuals. Cell reports, 36(8), 109570. |
| 32 | 31. Keehner, J., Binkin, N.J., Laurent, L.C., Pride, D. (2021). Resurgence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Highly Vaccinated Health System Workforce. The New England Journal of Medicine, 385, 1330-1332. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMc2112981. |
| 33 | 32. Chau, N. V. V., Ngoc, N. M., Nguyet, L. A., Quang, V. M., Ny, N. T. H., Khoa, D. B., … & OUCRU COVID-19 research group. (2021). An observational study of breakthrough SARSCoV-2 Delta variant infections among vaccinated healthcare workers in Vietnam. EClinicalMedicine, 41, 101143. |
| 34 | 33. Hetemäki, I., Kääriäinen, S., Alho, P., Mikkola, J., Savolainen-Kopra, C., Ikonen, N., Nohynek, H., Lyytikäinen, O. (2021). An outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant (B.1.617.2) in a secondary care hospital in Finland, May 2021. Eurosurveillance, 26, 2100636 (2021), https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.30.2100636. |
| 35 | 34. Shitrit, P., Zuckerman, N. S., Mor, O., Gottesman, B. S., & Chowers, M. (2021). Nosocomial outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in a highly vaccinated population, Israel, July 2021. Eurosurveillance, 26(39), 2100822. |
| 36 | 35. Acharya, C. B., Schrom, J., Mitchell, A. M., Coil, D. A., Marquez, C., Rojas, S., … & Havlir, D. (2021). No significant difference in viral load between vaccinated and unvaccinated, asymptomatic and symptomatic groups infected with SARSCoV-2 delta variant. MedRxiv. |
| 37 | 36. Riemersma, K. K., Grogan, B. E., Kita-Yarbro, A., Jeppson, G. E., O’Connor, D. H., Friedrich, T. C., & Grande, K. M. (2021). Vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals have similar viral loads in communities with a high prevalence of the SARS-CoV-2 delta variant. MedRxiv, 2021-07. |
| 38 | 37. Brown C.M., Vostok J., Johnson H., Burns, M., Gharpure, R., Sami, S., Sabo, R.T., Hall, N., Foreman, A., Schubert, P.L., Gallagher, G.R., Fink, T., Madoff, L.C., Gabriel, S.B.,MacInnis, B., Park, D.J., Siddle, K.J., Harik, V., Arvidson, D Brock-Fisher, T., Dunn, M., Kearns, A., Laney, A.S., 2021. Outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 infections, including COVID-19 vaccine breakthrough infections, associated with large public gatherings – Barnstable County, Massachusetts, July 2021. MMWR Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Reports 70, 1059- 1062. |
| 39 | 38. Servellita, V., Morris, M. K., Sotomayor-Gonzalez, A., Gliwa, A. S., Torres, E., Brazer, N., … & Chiu, C. Y. (2022). Predominance of antibody-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants in vaccine breakthrough cases from the San Francisco Bay Area, California. Nature microbiology, 7(2), 277-288. |
| 40 | 39. Subramanian, S. V., & Kumar, A. (2021). Increases in COVID-19 are unrelated to levels of vaccination across 68 countries and 2947 counties in the United States. European journal of epidemiology, 36(12), 1237-1240. |
| 41 | 40. Kirsch, S. (2021) “New Studies Show that the COVID Vaccines Damage your Immune System, Likely Permanently,” Steve Kirsch’s Newsletter, Dec. 24, 2021, https://stevekirsch.substack.com/p/new-stu-dy-shows-vaccines-must-be. |
| 42 | 41. Kirsch, S. (2022a). “Pfizer CEO says Two Covid Vaccine Doses Aren’t Enough for Omicron,” Steve Kirsch’s Newsletter Jan. 10, 2022, https://stevekirsch.subs-tack.com/p/pfizer-ceo-saystwo-covid-vaccine. |
| 43 | 42. 36. Ioannidis, J. P. (2021). Infection fatality rate of COVID-19 inferred from seroprevalence data. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 99(1), 19. |
| 44 | 43. Beattie, K.A. (2021) Worldwide Bayesian Causal Impact Analysis of Vaccine Administration on Deaths and Cases Associated with COVID-19: A BigData Analysis of 145 Countries. Department of Political Science University of Alberta Alberta, Canada. |
| 45 | 65. Psichogiou, M., Karabinis, A., Poulakou, G., Antoniadou, A., Kotanidou, A., Degiannis, D., … & Hatzakis, A. (2021). Comparative immunogenicity of BNT162B2 mRNA vaccine with natural covid-19 infection. medRxiv. |
| 46 | 44. Reuters, “EU Drug Regulator Expresses Doubt on Need for Fourth Booster Dose,” Jan. 11, 2022, https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/eu-drug-regulator-saysmore-data–needed-impact-omicron-vaccines-2022-01-11/. |
| 47 | 45. Kirsch, S. (2022b). “Top Israeli Immunologist Criticizes Pandemic Response in Open Letter,” Jan 13, 2022, Steve Kirsch’s Newsletter, https://stevekirsch.substack.com/p/top-israeli-immunologist–criticizes?r=15hae6&utm_campaign=post&utm_medium=email. |
| 48 | 46. Thorp, J.A., Renz, T., Northrup, C., et al. (2022). Patient betrayal: The Corruption of healthcare, informed consent and the physician – patient relationship. 0. https://www.doi.org/10.46766/tjegms. |
| 49 | 47. Doshi, P. 2020. Covid-19: Do many people have pre-existing immunity? 17 September 2020 BMJ 2020; 370 doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m3563 **** I believe the authors mis-referenced the study, I believe the study they meant to reference was this one |
| 50 | 48. Shimabukuro, T. T., Kim, S. Y., Myers, T. R., Moro, P. L Oduyebo, T., Panagiotakopoulos, L., … & Meaney-Delman, D. M. (2021). Preliminary findings of mRNA Covid-19 vaccine safety in pregnant persons. New England Journal of Medicine. |
| 51, 53, 85 | 83. Anand, P., & Stahel, V. P. (2021). The safety of Covid-19 mRNA vaccines: A review. Patient safety in surgery, 15(1), 1-9. |
| 52 | 89. Walsh, E.E., Frenck, R.W., Falsey, A.R. Jr., Kitchin, N., Absalon, J., Gurtman, A., Lockhart, S., Neuzil, K., Mulligan, M.J., Bailey, R. (2020). Safety and immunogenicity of two RNA-based Covid–19 vaccine candidates. New England Journal of Medicine, 383, 2439–50. |
| 54 | 90. Saito, S., Nakashima, A., Shima, T., & Ito, M. (2010). Th1/ Th2/Th17 and regulatory T?cell paradigm in pregnancy. American journal of reproductive immunology, 63(6), 601- 610. |
| 55 | 91. Helmo, F. R., Alves, E. A. R., Moreira, R. A. D. A., Severino, V. O., Rocha, L. P., Monteiro, M. L. G. D. R., … & Corrêa, R. R. M. (2018). Intrauterine infection, immune system and premature birth. The journal of maternal-fetal & neonatal medicine, 31(9), 1227-1233. |
| 56 | 49. Regev-Yochay, G., Gonen, T., Gilboa, M., Mandelboim, M., Indenbaum, V., Amit, S., … & Lustig, Y. (2022). Efficacy of a fourth dose of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine against omicron. New England Journal of Medicine, 386(14), 1377-1380. |
| 57 | 50. Regev-Yochay, G., Gonen, T., Gilboa, M., Mandelboim, M., Indenbaum, V., Amit, S., … & Lustig, Y. 4th Dose COVID mRNA Vaccines’ Immunogenicity & Efficacy Against Omicron VOC (preprint). |
| 58 | 51. Dopp, K, Seneff, S. (2022). COVID-19 and All-Cause Mortality Data by Age Group Reveals Risk of COVID Vaccine-Induced Fatality is Equal to or Greater than the Risk of a COVID death for all Age Groups Under 80 Years Oldas 2022: 1-21. |
| 59 | 52. Kostoff, R.N., Calina, D., Kanduc, D., Briggs, M.B., Vlachoyiannopoulos, P., Svistunov, A.A., Tsatsakis, A.. 2021. Why are we vaccinating children against COVID-19? Toxicology Reports. 8, 1665-1684. |
| 60 | 53. Goldberg, Y., Mandel, M., Bar-On, Y.M., Bodenheimer, O.,Freedman, L., Haas, E.J., Milo, R., Alroy-Preis, S., Ash, N., Huppert, A. (2021). Waning Immunity after the BNT162b2 Vaccine in Israel. New England Journal of Medicine, 385(24):e85. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2114228. |
| 61 | 54. Jo, D.-H., Minn, D., Lim, J., Lee, K.-D., Kang, Y.-M., Choe, K.-W., Kim, K.-N. (2021). Rapidly declining SARSCoV-2 antibody titers within 4 months after BNT162b2 vaccination. Vaccines, 9, 1145. |
| 62 | 55. Israel, A., Shenhar, Y., Green, I., Merzon, E., Golan- Cohen, A., Schäffer, A.A., Ruppin, E., Vinke,r S, Magen, E. (2021). Large-scale study of antibody titer decay following BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine or SARS-CoV-2 infection. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Aug 21:2021.08.19.21262111. doi: 10.1101/2021.08.19.21262111. Update in: Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Dec 31;10(1): PMID: 34462761; PMCID: PMC8404903. |
| 63 | 56. Binkin, N.J., Laurent, L.C., Pride, D., Longhurst, C.A., Abeles, S.R., Torriani, F.J. (2021). Resurgence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in highly vaccinated health system workforce. The New England Journal of Medicine. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2112981 |
| 64 | 57. Cromer, D., Steain, M., Reynaldi, A., Schlub, T.E., Wheatley, A.K., Juno, J.A., Kent, S.J., Triccas, J.A., Khoury, D.S., Davenport, M,P. (2022). Neutralising antibody titres as predictors of protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants and the impact of boosting: a meta-analysis. The Lancet Microbe 3, E52-E61 |
| 65 | 58. Krause P.R., Fleming, T.R.., Peto, R., Longini, I., Figueroa, J.P., Sterne, J.A.C., et al. (2021). Considerations in boosting COVID-19 vaccine immune responses. The Lancet 398, 1377 -10380. |
| 66 | 59. Lui, L., Luo, Y., Chu, H. et al. (2021) Striking antibody evasion manifested by the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-03826-3(2021). |
| 67 | 60. Hachmann, N. P., Miller, J., Collier, A. R. Y., Ventura, J. D., Yu, J., Rowe, M., … & Barouch, D. H. (2022). Neutralization escape by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA. 2.12. 1, BA. 4, and BA. 5. New England Journal of Medicine, 387(1), 86-88. |
| 68 | 61. Yamamoto, K. (2022). Adverse effects of COVID-19 vaccines and measures to prevent them. Virology Journal, 19(1), 1-3. |
| 69 | 62. Bryant, A., Lawrie, T. A., Dowswell, T., Fordham, E. J., Mitchell, S., Hill, S. R., & Tham, T. C. (2021). Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines. American journal of therapeutics, 28(4), e434. |
| 70 | 63. Bruno, R., Mccullough, P. A., Vila, T. F. I., Henrion-Caude, A., Garcia-Gasca, T., Zaitzeva, G. P., … & Acevedo-Whitehouse, K. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 mass vaccination: Urgent questions on vaccine safety that demand answers from international health agencies, regulatory authorities, governments and vaccine developers. Authorea Preprints. |
| 71 | 46. Thorp, J.A., Renz, T., Northrup, C., et al. (2022). Patient betrayal: The Corruption of healthcare, informed consent and the physician – patient relationship. 0. https://www.doi.org/10.46766/tjegms. |
| 72 | 64. Gat, I., Kedem, A., Dviri, M., Umanski, A., Levi, M., Hourvitz, A., & Baum, M. (2022). Covid?19 vaccination BNT162b2 temporarily impairs semen concentration and total motile count among semen donors. Andrology, 10(6), 1016-1022. |
| 73 | 75. Salamanna, F., Maglio, M., Landini, M.P., Fini, M. (2020). Body Localization of ACE-2: On the Trail of the Keyhole of SARS-CoV-2. Frontiers in Medicine, 7, https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2020.594495 |
| 76 | 74. Glas, M., Smola, S., Pfuhl, T., Pokorny, J., Bohle, R.M., Bücker, A., Kamradt J., Volk T. Fatal Multiorgan Failure Associated with Disseminated Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Infection: A Case Report. Case Reports in Critical Care, Volume 2012 doi: 10.1155/2012/359360 |
| 77 | 76. Jocher, G., Grass, V., Tschirner, S. K., Riepler, L., Breimann, S., Kaya, T., … & Lichtenthaler, S. F. (2022). ADAM10 and ADAM17 promote SARS?CoV?2 cell entry and spike proteinmediated lung cell fusion. EMBO reports, 23(6), e54305. |
| 78, 79 | 77. Pepe, A., Pietropaoli, S., Vos, M., Barba-Spaeth, G., & Zurzolo, C. (2022). Tunneling nanotubes provide a route for SARS-CoV-2 spreading. Science advances, 8(29), eabo0171. |
| 80, 88 | 78. Kelleni, M. T. (2021). SARS CoV-2 Vaccination Autoimmunity, Antibody Dependent Covid-19 Enhancement and Other Potential Risks: Beneath the Tip of the Iceberg. International Journal of Pulmonary & Respiratory Sciences, 5(2), 555658. |
| 81, 87 | 79. Lyons-Weiler, J. (2020). Pathogenic priming likely contributes to serious and critical illness and mortality in COVID-19 via autoimmunity. Journal of translational autoimmunity, 3, 100051. |
| 82, 89 | 80. Hasan, A., Al-Mulla, M. R., Abubaker, J., & Al-Mulla, F. (2021). Early insight into antibody-dependent enhancement after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 17(11), 4121-4125. |
| 83, 90 | 81. Classen, J. B. (2021). COVID-19 RNA based vaccines and the risk of prion disease. Microbiol Infect Dis, 5(1), 1-3. |
| 84, 91 | 82. Idrees, D., & Kumar, V. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interactions with amyloidogenic proteins: Potential clues to neurodegeneration. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 554, 94-98. |
| 86 | 84. Aldén, M., Olofsson Falla, F., Yang, D., Barghouth, M., Luan, C., Rasmussen, M., & De Marinis, Y. (2022). Intracellular reverse transcription of Pfizer BioNTech COVID-19 mRNA vaccine BNT162b2 in vitro in human liver cell line. Current issues in molecular biology, 44(3), 1115-1126. |
| 92 | 86. Finisterer J., Scorza, F.A. 2021. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are not free of neurological side effects. Acta Neurology Scandinavia 144, 109-110. doi: 10.1111/ane.13451 |
| 93 | 87. Kuvandik, A., Özcan, E., Serin, S., Sungurtekin, H. (2021). Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease After the COVID-19 Vaccination. Turkish Journal of Intensive Care. DOI: 10.4274/tybd.galenos.2021.91885. |
| 94 | 88. Serin, S., & Sungurtekin, H. (2021). Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease After the COVID-19 Vaccination. |
| 95 | 22. Kircheis, R. 2021. Coagulopathies after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 may be derived from a combined effect of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and adenovirus vector-triggered signaling pathways. International Journal of Molecular Science, |
| 96 | 92. Gundry, S. R. (2021). MRNA COVID vaccines dramatically increase endothelial inflammatory markers and ACS risk as measured by the PULS cardiac test: A warning. Circulation. |
| 97, 99 | 93. Bruno, R., Mccullough, P.A., Forcades, I., Vila, T. et al. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 mass vaccination: Urgent questions on vaccine safety that demand answers from international health agencies, regulatory authorities, governments and vaccine developers. Authorea, May 24, 2021. DOI: 10.22541/ au.162136772.22862058/v2. |
| 98 | 94. Blaylock, R. L. (2022). COVID UPDATE: What is the truth?.Surgical Neurology International, 13. |
| 100 | Conny Turni and Astrid Lefringhausen (2022) COVID-19 vaccines – An Australian Review. Journal of Clinical & Experimental Immunology. 7(3):491-508 21 Sep 2022 https://opastpublishers.com/open-access/covid-19-vaccines-an-australian-review.pdf |
Truth-seeker, ever-questioning, ever-learning, ever-researching, ever delving further and deeper, ever trying to 'figure it out'. This site is a legacy of sorts, a place to collect thoughts, notes, book summaries, & random points of interests.
DISCLAIMER: The information on this website is not medical science or medical advice. I do not have any medical training aside from my own research and interest in this area. The information I publish is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease, disorder, pain, injury, deformity, or physical or mental condition. I just report my own results, understanding & research.











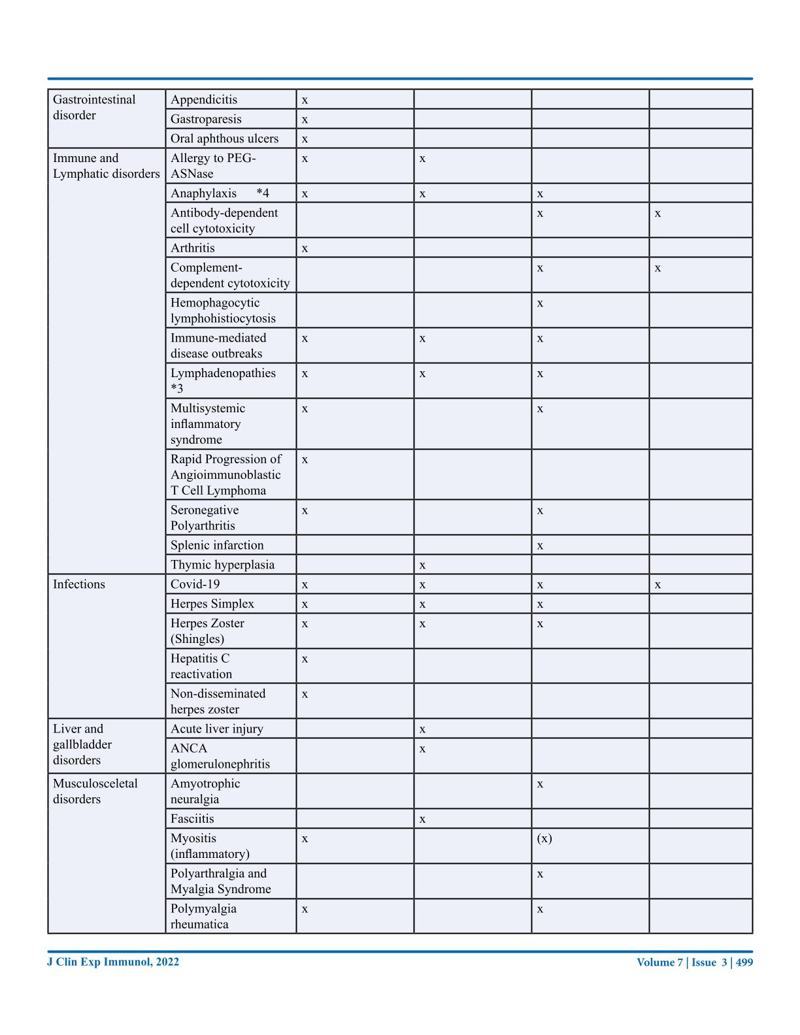

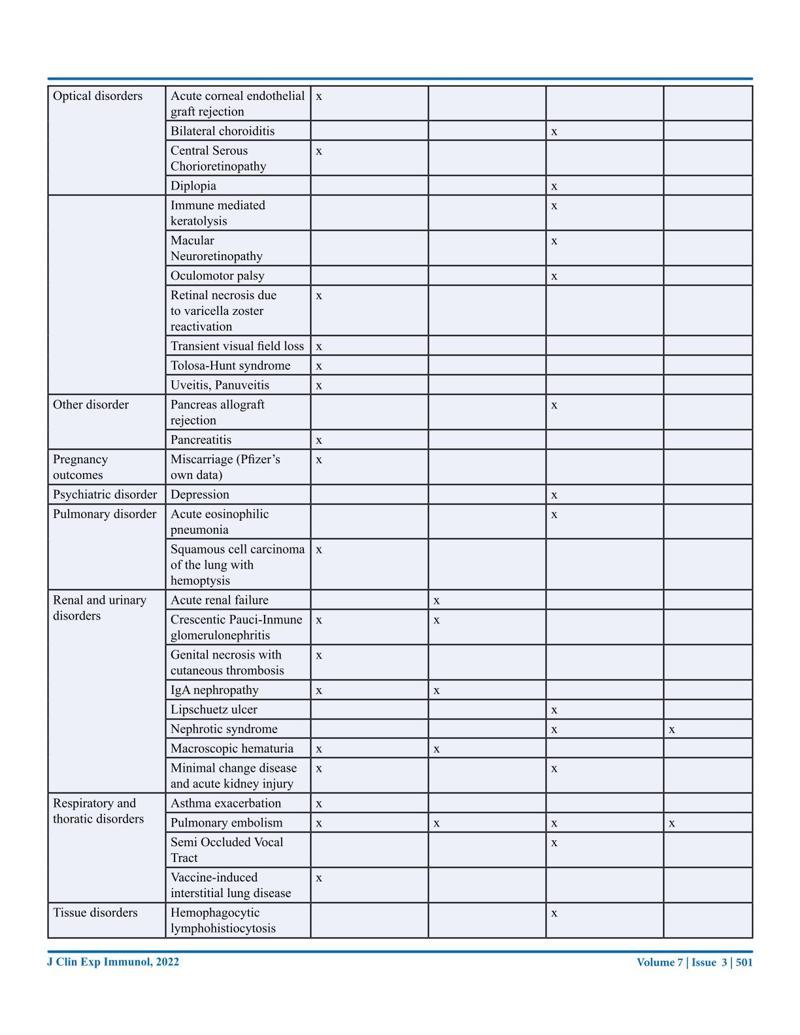
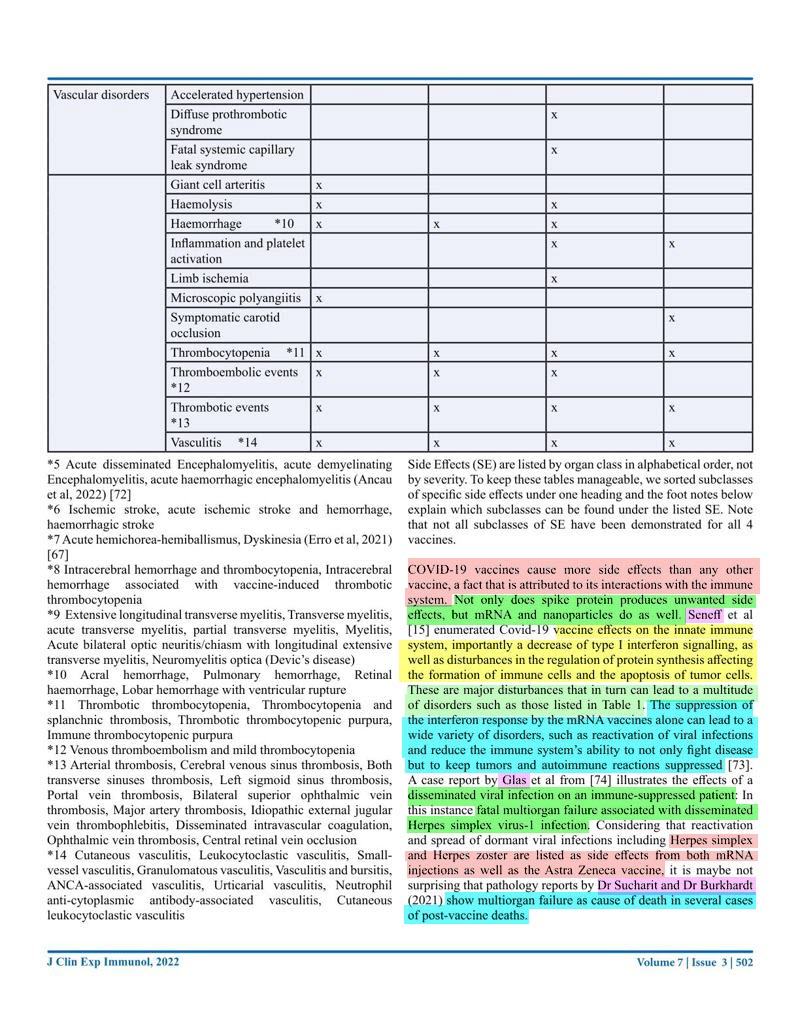








![[2013] The Hidden Agenda of Monsanto, GMOs, Rockefeller & Eugenics (Engdahl)](https://pennybutler.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/GeneticManipulation-324x437.jpg)
